Consequently they radiate heat into the sky to passively cool buildings at night.
Roof radiant heat loss to clear night sky formula.
Roof and wall heat gain cltd method.
For example the 1993 ashrae handbook of fundamentals mentions it nocturnal radiative cooling and provides a map of the u s.
A modified version of this formula from goforth et al.
We can also determine the radiative overcast night sky temperature as follows.
Below is an adjustment for air temperatures.
Q u a δt or in plain words the heat loss of an area of size a is determined by the u value of the materials and the difference in temperature between inside and out that is the difference in temperature of the two surfaces not the two air temperatures which might not be quite the same.
7 ru 1 where e emissivity of the outer surface 6 stefan boltzmann constant 7 outer surface temperature t y sky temperature.
397 9 24 90 25 0 25330 4 0 74 5 67 8 p tk εσ xe 0c radiation cooling time note that in these examples there was a 34 increase in downwelling sky radiation between an overcast 330 4 wm 2 and clear sky 246 6 wm 2.
The answer depends on the surface temperature the humidity the temperature gradient through the atmosphere and what exactly you mean by the temperature of the clear night sky.
Using 90 humidity the radiation from the sky is predicted to be 168 w m 2 53 27 btu hr ft 2.
Night sky radiant cooling nsrc has been something of a lost art even though it has been documented and discussed by hvac and solar heating professionals for many decades.
It s much closer to 273 k than 2 73 k.
The cltd tables are based on this condition.
If made sufficiently reflective to sunlight these materials can also achieve radiative cooling during the day.
The radiative night sky temperature is by your reference 3 9 celsius not 3 kelvin.
Correct cltd for a indoor temperature 78 o f b outdoor mean temperature 85 o f.
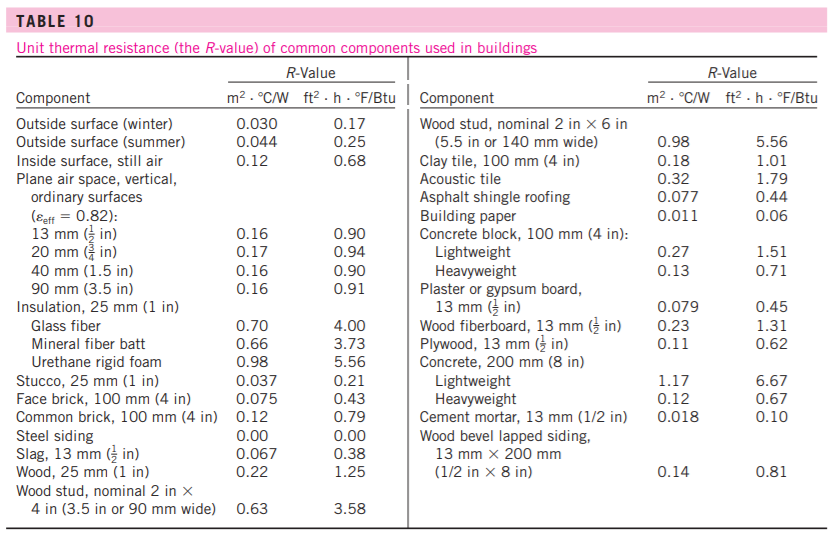
Composite wall r values up calculating wall heat loss example problems.
Otherwise we d be losing heat a lot faster.
Determine cltd for a roof number and b hour of the day.
For a clear sky the first term goes away and the formula becomes 8 78e 13xt 5 852xrh 0 07195.
The swinbank formula provides an ad hoc expression for the power radiated by the night sky.
The general heat loss formula is.
The most common radiative coolers found on buildings are white cool roof paint coatings which have solar reflectances of up to 0 94 and a thermal.
The 10 degrees f in my example is about 261 degrees r.
Is p text thermal 1 kc 2 8 78 times 10 13 t 5 852 rh 0 07195 where.
Showing cooling potential around the.
The roof is thus in radiative exchange with the earth s night sky not with deep space.
The net radiant heat loss from the outer surface of a low sloped roof can be expressed by.
Heat loss from roof 2 750 ft 2 6 100 f days 24 h day 22 ft 2 f h btu 18 30 mmbtu.
The microwave background radiation of the universe is about 3 kelvin but our atmosphere is much warmer than that.